The Visualization Toolkit (VTK) is an open-source,
freely available software system for 3D computer graphics, image
processing and visualization. VTK consists of a C++ class library and
several interpreted interface layers including Tcl/Tk, Java, and
Python. Kitware, whose team created and continues to extend the toolkit, offers professional support and consulting
services for VTK.
VTK supports a wide variety of visualization algorithms
including: scalar, vector, tensor, texture, and volumetric methods; and
advanced modeling techniques such as: implicit modeling, polygon
reduction, mesh smoothing, cutting, contouring, and Delaunay
triangulation.
VTK has an extensive information visualization framework, has a
suite of 3D interaction widgets, supports parallel processing, and
integrates with various databases on GUI toolkits such as Qt and Tk.
VTK is cross-platform and runs on Linux, Windows, Mac and Unix
platforms.
http://www.vtk.org/
Notes in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Fluid Mechanics, Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI)
Monday, March 31, 2014
Sunday, March 30, 2014
Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit (ITK): open-source, image analysis
Welcome to the National Library of Medicine Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit (ITK).
ITK is an open-source, cross-platform system that provides developers
with an extensive suite of software tools for image analysis.
Developed through extreme programming methodologies, ITK employs
leading-edge algorithms for registering and segmenting multidimensional
data. The goals for ITK include:
- Supporting the Visible Human Project.
- Establishing a foundation for future research.
- Creating a repository of fundamental algorithms.
-
Developing a platform for advanced product development.
- Support commercial application of the technology.
- Create conventions for future work.
-
Grow a self-sustaining community of software users and developers.
Saturday, March 29, 2014
2014 Conference on Computational Mechanics (CCM), May 16 to 18, 2014 , Suzhou, China
2014 Conference on Computational Mechanics (CCM) will be held on May 16 to 18, 2014 in Suzhou, China.
http://www.engii.org/workshop/CCM2014May/
 All the accepted papers will be
published by "Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics" (ISSN:
2327-4352), a peer-reviewed open access journal that can ensure the
widest dissemination of your published work. For more information,
please visit: http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp/
All the accepted papers will be
published by "Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics" (ISSN:
2327-4352), a peer-reviewed open access journal that can ensure the
widest dissemination of your published work. For more information,
please visit: http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp/
| Symposiums |
|
2014 Symposium on Fluid Mechanics (SFM)
|
| Starting from the liquid equilibrium theory established by Archimedes, to the Euler equation and Bernoulli's equation, fluid mechanics has experienced quite a long developing process. Nowadays, with the development of computer and advanced mathematics, computational fluid dynamics is widely applied in many important areas, and is a hot spot of research. This symposium will bring together scholars from around the world to discuss their new advances in the computational fluid dynamics. |
|
2014 Symposium on Rock Mechanics and Engineering (SRME)
|
| Rock mechanics is a practical and comprehensive discipline, having important and widespread applications in geology and civil engineering. The symposium will focus on the key technologies and new achievements on rock mechanics and engineering construction. |
|
2014 Symposium on Solid Mechanics (SSM)
|
| Solid mechanics has very extensive applications in modern engineering. From aircraft, ships, tanks, to houses, bridges, dams, atomic reactors, and even to household furniture, the structure design and calculation are based on the principle and calculation method of solid mechanics. The symposium will focus on the new progress in the field of solid mechanics and its development in the future. |
http://www.engii.org/workshop/CCM2014May/
 All the accepted papers will be
published by "Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics" (ISSN:
2327-4352), a peer-reviewed open access journal that can ensure the
widest dissemination of your published work. For more information,
please visit: http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp/
All the accepted papers will be
published by "Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics" (ISSN:
2327-4352), a peer-reviewed open access journal that can ensure the
widest dissemination of your published work. For more information,
please visit: http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp/
Thursday, March 27, 2014
Finite Element Methods for Flow Problems: Books & code
Jean Donea, Antonio Huerta, Finite Element Methods for Flow Problems, Wiley, 362 Pages, 2003
Review: The book mostly metioned the numerical methods and methods for solving differential equations. It compared many different methods for a flow problems.
The free Matlab code scripts are available for some examples in this book, http://www.lacan.upc.edu/huerta-web/exercises/Introduction/Introduction.htm
Review: The book mostly metioned the numerical methods and methods for solving differential equations. It compared many different methods for a flow problems.
The free Matlab code scripts are available for some examples in this book, http://www.lacan.upc.edu/huerta-web/exercises/Introduction/Introduction.htm
Wednesday, March 26, 2014
Endnote: bibliography, preferences
- Free Online endnote, can import the reference directly to microsoft word, and firefox, internet expolorer toolbar to save reference to the online bib. directly from the journal page, Use the EndNote plug-in to insert references, and format citations and bibliographies automatically while you write your papers in Word. This plug-in also allows you to save online references to your library in Internet Explorer for Windows, Firefox. http://www.myendnoteweb.com
- Instruction: Installing the EndNote "Cite While You Write" (CWYW) Tools into Microsoft Word for EndNote versions 4,5,6,7,8,9 and X., http://www.adeptscience.co.uk/kb/article/CC5E
- EndNote Web tab > Intert citations > type text for searching the matching reference
- You can insert reference as usual
- Select the citation to remove
- Ctrl + Shift + F9 : to remove the link with reference, it becomes text
- EndNote Web tab > Edit citations > deselect author, or year
Sunday, March 23, 2014
Trefethen's list of 13 classic papers in applied mathematics
Trefethen's list of 13 classic papers in applied mathematics
- J.W. Cooley and J.W. Tukey, "An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series," Math. Comp., 19 (1965), pp. 297–301.
- R. Courant, K. Friedrichs, and H. Lewy, "On the partial difference equations of mathematical physics," IBM J. Res. Develop., 11 (1967), pp. 215–234.
- A.S. Householder, "Unitary triangularization of a nonsymmetric matrix," J. Assoc. Comput. Mach., 5 (1958), pp. 339–342.
- C.F. Curtiss and J.O. Hirschfelder, "Integration of stiff equations," Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 38 (1952), pp. 235–243.
- C. de Boor, "On calculating with B-splines," J. Approximation Theory, 6 (1972), pp. 50–62.
- R. Courant, "Variational methods for the solution of problems of equilibrium and vibrations," Bull. Amer. Math. Soc., 49 (1943), pp. 1–23.
- G. Golub and W. Kahan, "Calculating the singular values and pseudo-inverse of a matrix," J. Soc. Indust. Appl. Math. Ser. B Numer. Anal., 2 (1965), pp. 205–224.
- A. Brandt, "Multi-level adaptive solutions to boundary-value problems," Math. Comp., 31 (1977), no. 138, pp. 333–390.
- M.R. Hestenes and E. Stiefel, "Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems," J. Research Nat. Bur. Standards, 49 (1952), pp. 409–436.
- R. Fletcher and M.J.D. Powell, "A rapidly convergent descent method for minimization," Comput. J., 6 (1963/1964), pp. 163–168.
- G. Wanner, E. Hairer, and S.P. Nørsett, "Order stars and stability theorems," BIT, 18 (1978), no. 4, pp. 475–489.
- N. Karmarkar, "A new polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming," Combinatorica, 4 (1984), no. 4, pp. 373–395.
- L. Greengard and V. Rokhlin, "A fast algorithm for particle simulations," J. Comput. Phys., 73 (1987), no. 2, pp. 325–348.
Friday, March 21, 2014
The 6th International Symposium on Microchemistry and Microsystems
The ISMM is a series of conferences that started in Kanazawa, Japan in 2009. It is now an annual international symposium which is held in Asia and Oceania regions: in Hong Kong in 2010, Seoul Korea in 2011, Taiwan in 2012, and Xiamen China in 2013. ISMM 2014 will be held in Singapore, from July 30th to August 1st. The symposium will focus on biomedicine, sensors and engineering. It covers a wide range of topics as stated below. We are anticipating more than 300 international renowned scholars and scientists to participate in this symposium which will be held in the vibrant city of Singapore.
Deadline for Abstract Submission March 28, 2014
Deadline for Author Acceptance Notification March 31, 2014
Deadline for Presenting Authors Registration April 15, 2014
Deadline for Full Length Paper Submission April 30, 2014
Deadline for Early-Bird Registration April 30, 2014
Meeting Dates 30 July - 1 August, 2014
http://www.ismm2014.net/
Deadline for Abstract Submission March 28, 2014
Deadline for Author Acceptance Notification March 31, 2014
Deadline for Presenting Authors Registration April 15, 2014
Deadline for Full Length Paper Submission April 30, 2014
Deadline for Early-Bird Registration April 30, 2014
Meeting Dates 30 July - 1 August, 2014
http://www.ismm2014.net/
Tuesday, March 18, 2014
Swiss-Singapore Workshop on Microfluidics 2014: Innovation and Opportunities
Swiss-Singapore Workshop on Microfluidics 2014: Innovation and Opportunities
Date : 02 Apr 2014 - 02 Apr 2014
Time : 9.00am
Venue : SIMTech Auditorium
Registration : Click here
Join the 7th Swiss-Singapore workshop to learn more about future manufacturing technologies from prominent Swiss and Singaporean experts.
Introduction
Following the successful events of the previous years, The Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech), the Centre Suisse d’Electronique et Microtechnique (CSEM) and swissnex will jointly host a workshop on Microfluidics. Delegates from Singapore and Switzerland, including some prominent industry leaders, will be in attendance to provide critical technological insights with the latest updates on the global Microfluidics industry, as well as to discuss upcoming innovation and future opportunities in the industry.
This workshop also showcases an array of microfluidics technologies, the services, products and competency of SIMTech Microfluidics Foundry for industry to tap on and develop capabilities. Potential collaborations and business opportunities could be established through the event.
Programme
8:30am Registration
9:00am Welcome Address
Dr Wang Zhiping, Director, SIMTech Research Programme
Dr Suzanne Hraba-Renevey, Executive Director, swissnex Singapore
9:10am Whole Cell Sensing Systems
Prof Nico de Rooij, EPFL Vice President, CSEM, SA, Switzerland
9:30am Innovation Factory
Mr Elmar Mock, Founder and Managing Partner, Creaholic SA, Switzerland
9:50am Microfluidics Opportunities with SIMTech: SMF and SMN
Dr Wang Zhiping, Director, SIMTech Research Programme
10:10am Signing Ceremony: Industry Collaboration on Microfluidics
10:20am Coffee Break & Exhibition
11:00am Industry Talk
11:20am Microfluidics for Protein ExtractionIndustry Talk
Dr Khuntontong Puttachat, Scientist, Microfluidics Manufacturing Programme, SIMTech
11:40am Industrialisation of Smart Systems
Dr Bahaa EI Roustom, Business Development Manager, CSEM SA, Switzerland
12:00pm Networking Lunch and Exhibition
1:30pm POC Molecular Diagnostics & DNA Sequencing: The Integration Rollercoaster!
Mr Jonathan O'Halloran, Chief Scientific Officer and Co-Founder, QuantuMDx Group, UK
1:50pm Sensor Controlled Pipetting, Accurate Liquid Transfers Validated in Real-time
Dr Bart van der Schoot, Vice President of R&D and Founder, Seyonic SA, Switzerland
2:10pm Ubiquitous Health Information from One Drop of Blood
Dr Luc Gervais, Chief Executive Officer and Founder, One Drop Diagnostics, Switzerland
2:30pm Fly-on-Chip: Microfluidics for Drosophila Neuroscience and Neuropharmacology
Dr Deepak Choudhury, Scientist, Microfluidics Manufacturing Programme, SIMTech
2:50pm Lateral Thinking: 2 Concrete Show-cases in Fluidic
Mr Luc Amgwerd, Intellectual Property Advisor, Creaholic SA, Switzerland
3:10pm End of Workshop
*3:30pm SIMTech Microfluidics Network Roundtable Meeting (RSVP by invitation only)
Registration
This workshop is free of charge. To reserve a place, please register online.Contact Us
For technical enquiries, please contact Dr Wang Zhenfeng, Email: zfwang@SIMTech.a-star.edu.sg; Tel: 6793 8596
Date : 02 Apr 2014 - 02 Apr 2014
Time : 9.00am
Venue : SIMTech Auditorium
Registration : Click here
Join the 7th Swiss-Singapore workshop to learn more about future manufacturing technologies from prominent Swiss and Singaporean experts.
Introduction
Following the successful events of the previous years, The Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech), the Centre Suisse d’Electronique et Microtechnique (CSEM) and swissnex will jointly host a workshop on Microfluidics. Delegates from Singapore and Switzerland, including some prominent industry leaders, will be in attendance to provide critical technological insights with the latest updates on the global Microfluidics industry, as well as to discuss upcoming innovation and future opportunities in the industry.
This workshop also showcases an array of microfluidics technologies, the services, products and competency of SIMTech Microfluidics Foundry for industry to tap on and develop capabilities. Potential collaborations and business opportunities could be established through the event.
Programme
8:30am Registration
9:00am Welcome Address
Dr Wang Zhiping, Director, SIMTech Research Programme
Dr Suzanne Hraba-Renevey, Executive Director, swissnex Singapore
9:10am Whole Cell Sensing Systems
Prof Nico de Rooij, EPFL Vice President, CSEM, SA, Switzerland
9:30am Innovation Factory
Mr Elmar Mock, Founder and Managing Partner, Creaholic SA, Switzerland
9:50am Microfluidics Opportunities with SIMTech: SMF and SMN
Dr Wang Zhiping, Director, SIMTech Research Programme
10:10am Signing Ceremony: Industry Collaboration on Microfluidics
10:20am Coffee Break & Exhibition
11:00am Industry Talk
11:20am Microfluidics for Protein ExtractionIndustry Talk
Dr Khuntontong Puttachat, Scientist, Microfluidics Manufacturing Programme, SIMTech
11:40am Industrialisation of Smart Systems
Dr Bahaa EI Roustom, Business Development Manager, CSEM SA, Switzerland
12:00pm Networking Lunch and Exhibition
1:30pm POC Molecular Diagnostics & DNA Sequencing: The Integration Rollercoaster!
Mr Jonathan O'Halloran, Chief Scientific Officer and Co-Founder, QuantuMDx Group, UK
1:50pm Sensor Controlled Pipetting, Accurate Liquid Transfers Validated in Real-time
Dr Bart van der Schoot, Vice President of R&D and Founder, Seyonic SA, Switzerland
2:10pm Ubiquitous Health Information from One Drop of Blood
Dr Luc Gervais, Chief Executive Officer and Founder, One Drop Diagnostics, Switzerland
2:30pm Fly-on-Chip: Microfluidics for Drosophila Neuroscience and Neuropharmacology
Dr Deepak Choudhury, Scientist, Microfluidics Manufacturing Programme, SIMTech
2:50pm Lateral Thinking: 2 Concrete Show-cases in Fluidic
Mr Luc Amgwerd, Intellectual Property Advisor, Creaholic SA, Switzerland
3:10pm End of Workshop
*3:30pm SIMTech Microfluidics Network Roundtable Meeting (RSVP by invitation only)
Registration
This workshop is free of charge. To reserve a place, please register online.Contact Us
For technical enquiries, please contact Dr Wang Zhenfeng, Email: zfwang@SIMTech.a-star.edu.sg; Tel: 6793 8596
Sunday, March 16, 2014
Code-aster: free code for studying of the behavior structural mechanics/ nuclear / electricity
Code_Aster is a code general practitioner for the study of the behavior structural mechanics.
The priority scope of application is that of the mechanics of deformable solids: that justifies the number of functionalities attached to the mechanical phenomenon. However, the study of the mechanical behavior of the industrial components requires beforehand the modelization of the stresses to which they are subjected, or of the physical phenomena which modify the parameters of
this behavior (fluid offsite intern or, temperature, phase change metallurgical, forces of electromagnetic origin...). For these reasons, Code_Aster
offers several possibilities of “sequence” of the mechanical phenomenon with the thermal or the acoustics, or with of other software, as well as a “kit” of construction of problems thermo-hydro-mechanics coupled.
Although Code_Aster can be used for many problems of structural analysis (code general practitioner), it was developed in particular to allow the study of the components of materials or machines used in the field of the electricity production and transmission. Thus the priority was given to the modelization of metal structures, géomatériaux and the reinforced concrete structure components.
One will find very few modelizations available for composites or elastomers.
The nonlinear analyses, as well in mechanics as in thermal, are in the middle of
Code_Aster : their effective drug required the tuning of powerful and relatively simple algorithms of use, even if the goal is not to make them function in “black box”. For the complex studies, it is thus necessary to understand the nature of the operations carried out by the code, in order to be able to control them in
an optimal way: one refers then to the theoretical notes giving the details of the modelizations and the methods, gathered in the Reference material.
http://www.code-aster.org
The priority scope of application is that of the mechanics of deformable solids: that justifies the number of functionalities attached to the mechanical phenomenon. However, the study of the mechanical behavior of the industrial components requires beforehand the modelization of the stresses to which they are subjected, or of the physical phenomena which modify the parameters of
this behavior (fluid offsite intern or, temperature, phase change metallurgical, forces of electromagnetic origin...). For these reasons, Code_Aster
offers several possibilities of “sequence” of the mechanical phenomenon with the thermal or the acoustics, or with of other software, as well as a “kit” of construction of problems thermo-hydro-mechanics coupled.
Although Code_Aster can be used for many problems of structural analysis (code general practitioner), it was developed in particular to allow the study of the components of materials or machines used in the field of the electricity production and transmission. Thus the priority was given to the modelization of metal structures, géomatériaux and the reinforced concrete structure components.
One will find very few modelizations available for composites or elastomers.
The nonlinear analyses, as well in mechanics as in thermal, are in the middle of
Code_Aster : their effective drug required the tuning of powerful and relatively simple algorithms of use, even if the goal is not to make them function in “black box”. For the complex studies, it is thus necessary to understand the nature of the operations carried out by the code, in order to be able to control them in
an optimal way: one refers then to the theoretical notes giving the details of the modelizations and the methods, gathered in the Reference material.
http://www.code-aster.org
Friday, March 14, 2014
Fluid mechanics/ dynamics: Definition
isothermal the temperature remains constant: ΔT = 0
homogeneous the similar / same nature
inviscid flow the flow of an ideal fluid assuming to have no viscosity
monolithic fully coupled
barotropic pressure and density are related by an equation of state, there is no dependent variable such as temperature
compressible fluid flow density vary from place to place
streamwise direction of a stream
no-slip BC fluid with a zero velocity related to the solid boundary
Taylor-Couette flow vicous flow in concentric rotating cylinders
Kelvin’s theorem a conservation law for angular momentum
Bubbly flow bubble flow is defined as a Two-Phase Flow where small bubbles are dispersed or suspended as discrete substances in a liquid continuum. (thermopedia)
Doublet (potential flow) fluid flow due to a source–sink combination
homogeneous the similar / same nature
inviscid flow the flow of an ideal fluid assuming to have no viscosity
monolithic fully coupled
barotropic pressure and density are related by an equation of state, there is no dependent variable such as temperature
compressible fluid flow density vary from place to place
streamwise direction of a stream
no-slip BC fluid with a zero velocity related to the solid boundary
Taylor-Couette flow vicous flow in concentric rotating cylinders
Kelvin’s theorem a conservation law for angular momentum
Bubbly flow bubble flow is defined as a Two-Phase Flow where small bubbles are dispersed or suspended as discrete substances in a liquid continuum. (thermopedia)
Doublet (potential flow) fluid flow due to a source–sink combination
Thursday, March 13, 2014
Useful tips in Ubuntu
- Show hidden files: at the browser, Ctrl + H
- Essential update: System > Update Manager
- Set up a startup applications: Setting button (gear shape on the upper right corner) > Starup Applications > Add> Add Name, Command (important, it is normally located at /usr/bin/)
- Add new repositories: System > Administration > Software Sources > Third Party Software > Add
- Check the package manager: System > Administration > Synaptic Package Manager
- Add bookmark for explorer: go to folder and Ctrl + D
Wednesday, March 12, 2014
CFD for Dispersed Multi-Phase Flows IV, April 3-4 2014, GE, Munich, Germany
CFD for Dispersed Multi-Phase Flows IV
April 3-4 2014, GE, Munich, Germany
SIG 12
Open for registration
Prof. Martin Sommerfeld, University Halle-Wittenberg, Germany
ERCOFTAC is proud to announce the fourth course on CFD for Dispersed Multi-Phase Flows, as part of its Best Practice Guidance series.Lecturers
-
Prof. Martin Sommerfeld, University Halle-Wittenberg, Germany
-
Prof. Ren Oliemans, Delft University, The Netherlands
-
Prof. Berend van Wachem, Imperial College, UK
Rationale
The simultaneous presence of several different phases in external or
internal flows such as gas, liquid and solid is found in daily life,
environment and numerous industrial processes. These types of flows are
termed multiphase flows, which may exist in different forms depending on
the phase distribution. Examples are gas-liquid transportation, crude
oil recovery, circulating fluidized beds, sediment transport in rivers,
pollutant transport in the atmosphere, cloud formation, fuel injection
in engines, bubble column reactors and spray
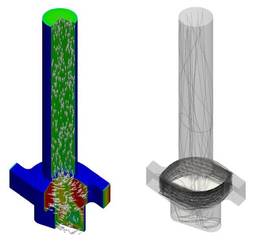
for food processing, to name only a few. As a result of the interaction
between the different phases such flows are rather complicated and very
difficult to describe theoretically. For the design and optimisation of
such multiphase systems a detailed understanding of the interfacial
transport phenomena is essential.
This course is rather unique as it is one of few in the community that
is specifically designed to deliver, a) a best practice guidance and b)
the latest trends, in CFD for dispersed multi-phase flows.
The course appeals to researchers and engineers involved in projects
requiring CFD for (wall-bounded) turbulent dispersed multiphase flows
with bubbles, drops or particles. Moreover, delegates are offered
the opportunity to present their work via 10 minute presentations ,
thereafter, the lecturers can offer prospective solution.
url
http://www.ercoftac.org/events/industryevents_2014/cfd_for_dispersed_multi-phase_flows_iv/Tuesday, March 11, 2014
HPCC-2014 - IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Communications, Paris
HPCC Conference
Important Dates
Paper submission: 28 April 2014
Notification of acceptance: 23 June 2014
Camera ready due: 15 July 2014
Introduction
With the rapid growth in computing and communications technology, the past decade has witnessed a proliferation of powerful parallel and distributed systems and an ever-increasing demand for practice of high performance computing and communications (HPCC). HPCC has moved into the mainstream of computing and has become a key technology in determining future research and development activities in many academic and industrial branches, especially when the solution of large and complex problems must cope with very tight timing schedules.
The HPCC-2014 conference is the 16th IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Communications. It will provide a forum for engineers and scientists in academia, industry, and government to address the resulting profound challenges and to present and discuss their new ideas, research results, applications and experience on all aspects of high performance computing and communications. HPCC-2014 is sponsored by IEEE, IEEE Computer Society, and IEEE Technical Committee on Scalable Computing (TCSC).
The HPCC-2014 conference is the next event in a series of highly successful international conferences on high performance computing and communications (HPCC), previously held as HPCC-13 (Zhangjiajie, China, November 2013), HPCC-12 (Liverpool, UK, June 2012), HPCC-11 (Banff, Canada, September 2011), HPCC-10 (Melbourne, Australia, September 2010), HPCC-09 (Seoul, Korea, June 2009), HPCC-08 (Dalian, China, September 2008), HPCC-07 (Houston, USA, September 2007), HPCC-06 (Munich, Germany, September 2006), HPCC-05 (Naples, Italy, September 2005), HPCN-04 (Tokyo, Japan, December 2004), PACT-SHPSEC03 (New Orleans, USA, September 2003), PACT-SHPSEC02 (Charlottesville, USA, September 2002), HPCA-01 (Nova Scotia, Canada, November 2001), HPNCA-00 (Delft, The Netherlands, May 2000), HPNCA-99 (Amsterdam, The Netherlands, April 1999).
http://conference.hpcc2014.studiocheik.fr/
Important Dates
Paper submission: 28 April 2014
Notification of acceptance: 23 June 2014
Camera ready due: 15 July 2014
Introduction
With the rapid growth in computing and communications technology, the past decade has witnessed a proliferation of powerful parallel and distributed systems and an ever-increasing demand for practice of high performance computing and communications (HPCC). HPCC has moved into the mainstream of computing and has become a key technology in determining future research and development activities in many academic and industrial branches, especially when the solution of large and complex problems must cope with very tight timing schedules.
The HPCC-2014 conference is the 16th IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Communications. It will provide a forum for engineers and scientists in academia, industry, and government to address the resulting profound challenges and to present and discuss their new ideas, research results, applications and experience on all aspects of high performance computing and communications. HPCC-2014 is sponsored by IEEE, IEEE Computer Society, and IEEE Technical Committee on Scalable Computing (TCSC).
The HPCC-2014 conference is the next event in a series of highly successful international conferences on high performance computing and communications (HPCC), previously held as HPCC-13 (Zhangjiajie, China, November 2013), HPCC-12 (Liverpool, UK, June 2012), HPCC-11 (Banff, Canada, September 2011), HPCC-10 (Melbourne, Australia, September 2010), HPCC-09 (Seoul, Korea, June 2009), HPCC-08 (Dalian, China, September 2008), HPCC-07 (Houston, USA, September 2007), HPCC-06 (Munich, Germany, September 2006), HPCC-05 (Naples, Italy, September 2005), HPCN-04 (Tokyo, Japan, December 2004), PACT-SHPSEC03 (New Orleans, USA, September 2003), PACT-SHPSEC02 (Charlottesville, USA, September 2002), HPCA-01 (Nova Scotia, Canada, November 2001), HPNCA-00 (Delft, The Netherlands, May 2000), HPNCA-99 (Amsterdam, The Netherlands, April 1999).
http://conference.hpcc2014.studiocheik.fr/
Monday, March 10, 2014
Solid Mechanics
BOOKS
- Madhukar Vable, Mechanics of Materials, Second Edition, Michigan Technological University http://www.me.mtu.edu/~mavable/MoM2nd.htm
- Stephen Timoshenko, and S. Woinowsky-Krieger, Theory of plates and shells, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1959, 580p, http://155.207.34.6/files/Timoshenko.pdf
PEOPLE
- Ted Belytschko, Walter P. Murphy Professor and McCormick Professor, Northwestern University, Department of Mechanical Engineering, http://www.tam.northwestern.edu/people/belytchko.html
- Tayfun E. Tezduyar, James F. Barbour Professor in Mechanical Engineering, Rice University, http://www.tafsm.org/~tezduyar/
- Thomas JR Hughes, Professor of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, Computational and Applied Mathematics, http://users.ices.utexas.edu/~hughes/
- Klaus-Jürgen Bathe, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, http://meche.mit.edu/people/index.html?id=10
- W.K. Liu,Walter P. Murphy Professor, Northwestern University, Department of Mechanical Engineering, http://www.tam.northwestern.edu/wkl/liu.html
- Emeritus Professor Gordon Williams, (Fracture Mechanics), http://www.imperial.ac.uk/AP/faces/pages/read/Home.jsp?person=g.williams
- Eugenio Oñate Ibañez de Navarra, Director of International Center for Numerical Methods in Engineering (CIMNE), http://www.cimne.com/eo/spacehome/1/0#
- David J. Benson, Professor, Structural Engineering, UC San Diego http://www.jacobsschool.ucsd.edu/faculty/faculty_bios/index.sfe?fmp_recid=63
- Ken P. Chong, National Institute of Standards and Technology [NIST] , George Washington University,
- Yoichiro Matsumoto, Executive Vice President / Vice-president / Professor, Mechanobioengineering, Tokyo, Fluid, multiphase, http://www.bioeng.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/faculty/27_matsumoto.html
- Shih Choon Fong, ex-President NUS, nonlinear fracture mechanics and computational methods for fracture analyses
- Allan F. Bower, also have free code in Maple, Matlab, Fortran http://solidmechanics.org/
Award
- Ted Belytschko Applied Mechanics Award
- O. C. Zienkiewicz Medal
- The world's most highly cited engineering researchers
TERMS
- Neo-Hookean solid, hyperelastic material model
- Mooney–Rivlin solid
- Finite Strain Theory/ Large Strain Theory/ Large Deformation Theory
Sunday, March 9, 2014
HVAC Notes
Lectures, Notes:
- Heating and Air Conditioning, http://www.engr.ipfw.edu/~renie/ME421%20Page/index421.html
- BBSE2008 Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Engineering, http://www.mech.hku.hk/bse/bbse2008/resources.htm
Saturday, March 8, 2014
Eclipse Platform: Free Platform for multi Programming
C/C++ : Eclipse platform
Short Cut
Ctrl + B : Build All
Ctrl + F11 : Run
F11 : Debug
Ctrl + H : Search
Ctrl + Alt + G : Workspace
Ctrl + Z : Redo
Ctrl + U : Undo Typing
Shift + Alt + N : New
Ctrl + S : Save
Shift + Ctrl + S : Save All
Alt + Enter : Properties
F5 : Refresh
Ctrl + W : Close
Shift + Ctrl + W : Close All
Ctrl + P : Print
Utilities
Short Cut
Ctrl + B : Build All
Ctrl + F11 : Run
F11 : Debug
Ctrl + H : Search
Ctrl + Alt + G : Workspace
Ctrl + Z : Redo
Ctrl + U : Undo Typing
Shift + Alt + N : New
Ctrl + S : Save
Shift + Ctrl + S : Save All
Alt + Enter : Properties
F5 : Refresh
Ctrl + W : Close
Shift + Ctrl + W : Close All
Ctrl + P : Print
Utilities
- To show building process: Window >Show View >other >General >Progress
- Change font in eclipse: Window > Preferences > General > Appearance > Colors and Fonts > C/C++ > Editor > C/C++ Editor Text Font
Friday, March 7, 2014
Applied Mathematics and Physics: Handouts/ Lectures/ Book
Free to download
- Matthias Heil, Functions of two variables and PDEs, http://www.maths.manchester.ac.uk/~mheil/Lectures/2M1/index.html
- Matthias Heil, Calculus and Applications -- Part 1: ODE, http://www.maths.manchester.ac.uk/~mheil/Lectures/FirstYearODEs/index.html
- J. David Logan, Applied Mathematics, third edition, https://elearning.fesb.hr/pluginfile.php/63405/mod_resource/content/2/%5BJ._David_Logan%5D_Applied_Mathematics,_Third_Editio%28BookFi.org%29.pdf
Thursday, March 6, 2014
PhD Studentship - Sound and Vibration Research - Aeroacoustics
PhD Studentship - Sound and Vibration Research - Aeroacoustics
University of Southampton · Institute of Sound and Vibration Research (ISVR)
University of Southampton · Institute of Sound and Vibration Research (ISVR)
United Kingdom, Southampton
PhD Studentship
Spectral broadening in aeroacoustics
Applications are invited for a PhD research student working on Aeroacoustics. The project is supported by Rolls-Royce plc and will be supervised within the Rolls-Royce University Technology Centre (UTC) in Gas Turbine Noise at the Institute of Sound and Vibration Research (ISVR) at the University of Southampton. The successful applicant will join a strong team at the UTC working on new research to reduce aircraft noise.
Reducing the environmental impact of civil aviation is critical to the growth of air transport and to the future of the aircraft industry. Ambitious environmental goals for the industry have been set by the Advisory Council for Aeronautics Research in Europe (ACARE). These include reducing by 97% (15 dB) the noise from civil aircraft by 2050.
Work undertaken in this project will focus on scattering of tonal noise, produced by the fan and turbine, by the turbulent exhaust jet from an aero-engine. The key aim will be to acquire a model-scale experimental database of measurements of the scattering obtained in the laboratory. There is currently no such database available; the data will be used for validation purposes to support the development of robust, validated prediction methods, as well as to improve our understanding of the scattering phenomenon. The work will include experimental fluid dynamics, data appraisal, and some theoretical modelling.
The studentship would provide support at standard EPSRC rates (currently around £13,900 p.a.) and EU/UK tuition fees for three years. The start date will be 1st October 2014, or earlier with agreement. Applicants should have a good first degree in a relevant science or engineering subject. Ideally the candidate should have some experience in experimental fluid dynamics and/or aeroacoustics.
Details of how to apply online may be found at: http://www.southampton.ac.uk/engineering/postgraduate/research_degrees/apply.page
If you wish to discuss any details of the project informally, please contact Dr Alan McAlpine, Acoustics research group, Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton by using the Apply button below. Please quote reference number: ISVR-FDAG-103
Spectral broadening in aeroacoustics
Applications are invited for a PhD research student working on Aeroacoustics. The project is supported by Rolls-Royce plc and will be supervised within the Rolls-Royce University Technology Centre (UTC) in Gas Turbine Noise at the Institute of Sound and Vibration Research (ISVR) at the University of Southampton. The successful applicant will join a strong team at the UTC working on new research to reduce aircraft noise.
Reducing the environmental impact of civil aviation is critical to the growth of air transport and to the future of the aircraft industry. Ambitious environmental goals for the industry have been set by the Advisory Council for Aeronautics Research in Europe (ACARE). These include reducing by 97% (15 dB) the noise from civil aircraft by 2050.
Work undertaken in this project will focus on scattering of tonal noise, produced by the fan and turbine, by the turbulent exhaust jet from an aero-engine. The key aim will be to acquire a model-scale experimental database of measurements of the scattering obtained in the laboratory. There is currently no such database available; the data will be used for validation purposes to support the development of robust, validated prediction methods, as well as to improve our understanding of the scattering phenomenon. The work will include experimental fluid dynamics, data appraisal, and some theoretical modelling.
The studentship would provide support at standard EPSRC rates (currently around £13,900 p.a.) and EU/UK tuition fees for three years. The start date will be 1st October 2014, or earlier with agreement. Applicants should have a good first degree in a relevant science or engineering subject. Ideally the candidate should have some experience in experimental fluid dynamics and/or aeroacoustics.
Details of how to apply online may be found at: http://www.southampton.ac.uk/engineering/postgraduate/research_degrees/apply.page
If you wish to discuss any details of the project informally, please contact Dr Alan McAlpine, Acoustics research group, Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton by using the Apply button below. Please quote reference number: ISVR-FDAG-103
Reference number: ISVR-FDAG-103
Wednesday, March 5, 2014
Monte Carlo Method
Monte Carlo Methods (MCM)
Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) method
Applied both in computational engineering and finance
PEOPLE
Books/ Lecture Notes:
Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) method
Applied both in computational engineering and finance
PEOPLE
- Graeme Bird, Emeritus Prof of Aeronautics, University of Sydney, proposed the Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) method,
- Mike Giles, Professor of Scientific Computing, Oxford, http://www.maths.ox.ac.uk/contact/details/gilesm
- GA Birth, http://www.aeromech.usyd.edu.au/dsmc_gab/
- Prof. Einar Kruis, Institute of technology for Nanostructures, Universität Duisburg-Essen, (CFD+Monte Carlo) link
Books/ Lecture Notes:
- D.P. Kroese, T. Taimre, Z.I. Botev (2011). Handbook of Monte Carlo Methods, Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
- Lecture Notes: Monte Carlo Methods, http://www.maths.uq.edu.au/~kroese/mccourse.pdf
Code: free / commercial
- Matlab, source program, http://www.maths.uq.edu.au/~kroese/montecarlohandbook/
Tuesday, March 4, 2014
LS-PrePost: free pre and post-processor
LS-PrePost is an advanced pre and post-processor that is delivered free with LS-DYNA. The user interface is designed to be both efficient and intuitive. LS-PrePost runs on Windows, Linux, and Unix utilizing OpenGL graphics to achieve fast rendering and XY plotting. The latest builds can be downloaded from LSTC's FTP Site.
http://www.lstc.com/lspp/
- Key Pre-Processing Features:
 Comprehensive LS-DYNA Keyword Support
Comprehensive LS-DYNA Keyword Support All new CAD engine in LS-PrePost 3
All new CAD engine in LS-PrePost 3 Faster rendering engine in LS-PrePost 4
Faster rendering engine in LS-PrePost 4 Interactive Entity (Keyword) Creation
Interactive Entity (Keyword) Creation Meshing Tools
Meshing Tools Surface Meshing
Surface Meshing Tool Meshing
Tool Meshing 2D Meshing
2D Meshing Tet Meshing
Tet Meshing Block Meshing
Block Meshing Mesh Morphing
Mesh Morphing Special Applications
Special Applications Metal Forming
Metal Forming Roller Hemming
Roller Hemming Airbag Folding
Airbag Folding Dummy Positioning
Dummy Positioning Seatbelt Fitting
Seatbelt Fitting Penetration Checking
Penetration Checking Model Checking
Model Checking
- Key Post-Processing Features:
 D3PLOT Animation
D3PLOT Animation Eigen Mode Animation
Eigen Mode Animation BINOUT Processing
BINOUT Processing DYNAIN Generation
DYNAIN Generation Section Analysis
Section Analysis Fringe Plotting
Fringe Plotting ASCII Plotting
ASCII Plotting Time History Plotting
Time History Plotting Particle Visualization
Particle Visualization Fluid Visualization
Fluid Visualization
Monday, March 3, 2014
TOPAZ3D
TOPAZ3D is a vectorized, three-dimensional, implicit finite element computer code for heat transfer analysis. It can be used to solve for the steady-state or transient temperature field in three-dimensional geometries. Users can model chemical reaction kinetics and allow for any type of functional representation of boundary conditions and internal heat generation. It can solve problems of diffuse and specular band radiation in an enclosure coupled with conduction in the material surrounding the enclosure. Additional features include thermal contact resistance across an interface, bulk fluids,
phase change, and energy balances.
Energy Science and Technology
Software Center
P.O. Box 1020
Oak Ridge, TN 37831-1020, USA
Contact: Berta Perez
Fax: (625) 576-2865
Phone: (615) 576-5637
E-mail: estsc@adonis.osti.gov
phase change, and energy balances.
Energy Science and Technology
Software Center
P.O. Box 1020
Oak Ridge, TN 37831-1020, USA
Contact: Berta Perez
Fax: (625) 576-2865
Phone: (615) 576-5637
E-mail: estsc@adonis.osti.gov
Sunday, March 2, 2014
Open Access/ Online learning courses/ websites
- Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform Coursera, www.coursera.org
- MIT open courseware, http://ocw.mit.edu
- Khan Academy, www.khanacademy.org
- Ted, www.ted.com
- Nanyang Technological University, Open access, DR-NTU, http://dr.ntu.edu.sg/
Saturday, March 1, 2014
SolidWorks Keyboard Shortcuts
File
Ctrl+ N New
Ctrl+ O Open
Ctrl+ W Open from web folder
Ctrl+ D Make a drawing from part or assy
Ctrl+ A Make a new assy from part or assy
Ctrl+ S Save
Ctrl+ P Print
Edit
Ctrl+ Z Undo
Ctrl+ Y Redo
ENTER Repeat Last Command
Ctrl+ X Cut
Ctrl+ C Copy
Ctrl+ V Paste
DELETE Delete
Ctrl+ B Rebuild
Ctrl+ Q Forced Rebuild
View
Arrow Keys Rotate the model
SHFT+ Arrow Keys Rotate the model 90º
ALT+ Arrow Keys Rotate the model CW or CCW
Ctrl+ Arrow Keys Pan the model
Ctrl+ R Redraw
SPACEBAR Orientation
F Zoom to Fit
Ctrl+SHFT+ Z Undo View Change
Ctrl+ F1 View Task Pane
F3 View Quick Snaps
Z Zoom Out One Step
SHFT+ Z Zoom In One Step
Tools
L Line
Ctrl+M Mate Diagnostics
Others
Ctrl+ 1 Front
Ctrl+ 2 Back
Ctrl+ 3 Left
Ctrl+ 4 Right
Ctrl+ 5 Top
Ctrl+ 6 Bottom
Ctrl+ 7 Iso
Ctrl+ 8 Normal to
A Command Option Toggle
C Expand/Collapse Tree
E Filter Edges
V Filter Vertices
X Filter Faces
N Next Edge
Y Accept Edge
F1) (Help
SHFT+ F1 What's this?
F2 Name edit mode
Ctrl+TAB+ Cycle between documents-forward
Ctrl+SHFT+TAB+ Cycle between documents-backwards
Ctrl+F6 Next window
Ctrl+F4 Close window
F5 Toggle Selection Filter Toolbar
F6 Toggle Selection Filter
Arrow Keys Move Drawing View Up, Down, Left, Right
Ctrl+ Q Force Regen To Top Level Of Assy
Ctrl+ALT+SHFT+ H Make Horizontal
ALT+R Edit dimension properties
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)